Lysine is the first limiting amino acid in swine diets based on corn and soybean meal. Lysine requirements for pigs are affected by growth rate and lean deposition rate, which in turn are affected by sex, genetics, age, and other factors. An experiment was conducted to determine the requirement for standardized ileal digestible (SID) lysine in 25 to 50 kg growing gilts.
Experimental design
Seventy gilts with an average initial body weight of 24.54 were used in the experiment. Gilts were the offspring of G-Performer boars mated to F-25 females (Genetiporc, Alexandria, MN). Five diets based on corn and soybean meal were formulated. The amount of soybean meal in the diets was varied to create diets containing calculated SID lysine levels of 0.80%, 0.93%, 1.06%, 1.19%, and 1.32%. Pigs were weighed at the beginning and at the conclusion of the experiment on day 33. Daily feed rations and leftover feed were also weighed, and these weights were used to calculate average daily gain, average daily feed intake, and gain:feed ratio for each treatment group.
Results
No difference in average daily feed intake was observed between pigs fed diets containing different concentrations of SID lysine (Table 1).
Average daily gain increased quadratically (P < 0.05) as the concentration of SID lysine in the diets increased. A quadratic line was fitted to the data (Figure 1). Using the asymptote of the line, the optimal SID lysine requirement for maximizing average daily gain was estimated to be 1.08%.
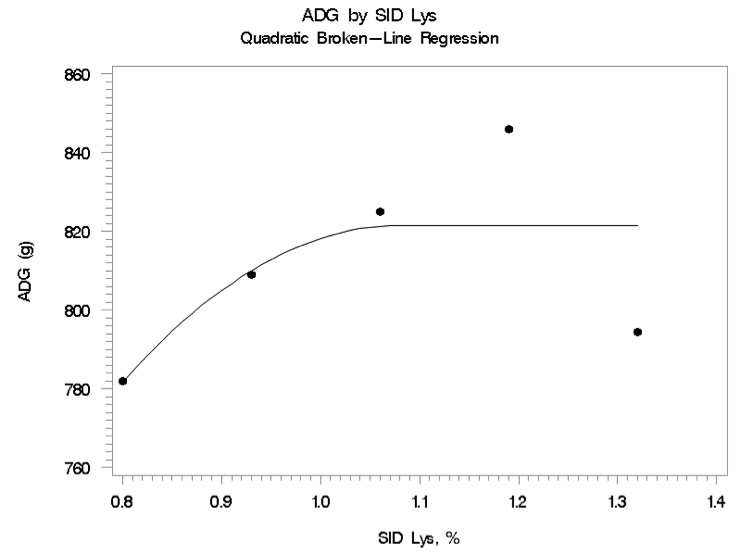
Figure 1. Fitted quadratic plot of average daily gain as a function of SID lysine
A linear increase (P < 0.05) was observed in the gain:feed ratio as the concentration of lysine in the diets increased (Table 1). Using a broken-line regression, the optimal SID lysine requirement for maximizing gain:feed was estimated to be 1.10% (Figure 2).
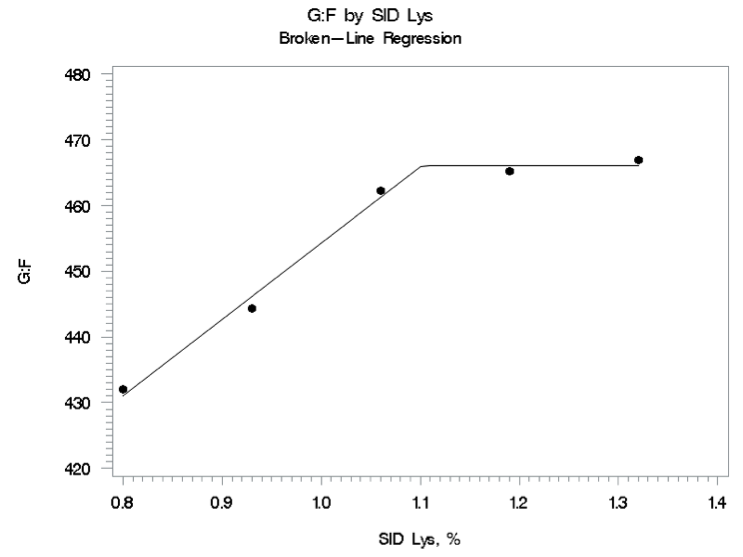
Figure 2. Fitted broken-line plot of gain:feed as a function of SID lysine
Averaging the values obtained by plotting the data for average daily gain and gain:feed yielded an estimated SID lysine requirement of 1.09%.
The requirement determined in this study was greater than that suggested in the most recent NRC (2012). There are a number of possible reasons for this result. The experiment included only gilts, and results of previous research have indicated that gilts require more lysine than barrows. In addition, the pigs used in this study were from a particular Genetiporc line that is optimized for maximum growth rates. These pigs' rate of lean deposition, and thus their lysine requirements, may be greater than average. It is also possible that the composition of the diets was a factor. Experiments are often conducted using synthetic diets, which may not accurately replicate the protein and energy levels in corn. The current experiment used corn-soybean diets similar to those used in commercial production, and thus the requirements determined may be more indicative of the requirements for commercially raised pigs.
Key points
- Values of 1.08% and 1.10% for the requirement for SID lysine were obtained by optimizing for average daily gain and gain:feed ratio, respectively.
- The requirement for SID lysine for 25 to 50 kg growing gilts was estimated in this study at 1.09%.
- The requirement determined in this study was greater than that suggested in the most recent NRC. This may be due to the sex and genetics of the pigs used in the study, as well as the composition of the diets. All of these factors are relevant when determining lysine requirements.
Table 1. Growth performance of pigs fed increasing levels of standardized ileal digestible lysine
|
|
Standardized ileal digestible lysine, % |
Contrasts (P-value) |
|||||
|
|
0.80 |
0.93 |
1.06 |
1.19 |
1.32 |
Linear |
Quadratic |
|
Initial BW, kg |
28.07 |
28.11 |
28.05 |
28.10 |
27.98 |
0.52 |
0.54 |
|
ADG, g |
782 |
809 |
825 |
846 |
794 |
0.27 |
0.03 |
|
ADFI, g |
1,758 |
1,826 |
1,738 |
1,775 |
1,658 |
0.12 |
0.20 |
|
G:F |
432 |
444 |
462 |
465 |
467 |
0.00 |
0.28 |
|
Final BW, kg |
53.60 |
54.52 |
54.99 |
55.74 |
53.92 |
0.33 |
0.03 |
This report is based on unpublished research by J. K. Mathai and H. H. Stein.