Soybean meal is the principal amino acid (AA) source in diets for pigs, and it is recognized that the AA profile of soybean meal is superior to that of other oilseed meals. However, new varieties that have different characteristics are sometimes developed and an example of such a new variety is the Photoseed variety of soybeans that captures more carbon and sunlight leading to a more nutrient rich ingredient and a reduced footprint from crop production. There is, however, no information about the nutritional value of the soybean meal produced from the Photoseed variety of soybeans. Therefore, the objective of this research was to test the hypothesis that the apparent ileal digestibility (AID) of crude protein (CP) and AA, and the standardized ileal digestibility (SID) of CP and AA are not different in soybean meal produced from Photoseed soybeans compared with control soybean meal when fed to pigs.
Material and methods
Soybean expellers produced from either the Photoseed variety or a control variety (PhotoSeed, Zeakal Inc., San Diego, CA) were use. Nine barrows (initial BW: 30 ± 1.5 kg) that had a T-cannula installed in the distal ileum were used. Pigs were placed in 1.2 × 1.5 m individual pens equipped with a self-feeder, a nipple waterer, and fully slatted tri-bar floors. Pigs were allotted to a replicated 3 × 3 Latin square design with 3 diets and 3 periods of 7 d each. There were 3 pigs per diet in each period for a total of 9 observations per treatment. Each of the 2 soybean sources were included in one diet and a nitrogen-free diet was used to measure basal endogenous losses of AA. Vitamins and minerals were included in all diets to meet or exceed the estimated nutrient requirements for growing pigs. All diets contained 0.40% chromic oxide as an indigestible marker. A sample of each diet was collected at the time of diet mixing.
Each experimental period lasted 7 d. The initial 5 d of each period was considered an adaptation period. Ileal digesta were collected on d 6 and 7 for 9 h using standard procedures. At the conclusion of the experiment, ileal digesta samples were thawed, mixed within animal and diet, and a subsample was collected for analysis. Ileal digesta samples were lyophilized and finely ground and analyzed for CP and AA.
Results and discussion
Concentration of GE, CP, crude fat, P and Ca were greater in the Photoseed soybean meal than in the control (Table 1). In contrast, the concentration of total dietary fiber (TDF) was lower in the Photoseed ingredient compared with the control. Concentrations of phytic acid and trypsin inhibitors were also greater in the Photoseed ingredient than in the control ingredient. The concentration of most of the indispensable AA was also greater in the Photoseed ingredient compared with the control.
The SID of total indispensable AA were greater (P < 0.05) in the control soybean meal compared with the Photoseed soybean meal (Table 2). However, SID of Arg, Ile, and Lys were not different between the two ingredients, but the SID of the other indispensable AA were greater in the control soybean meal than in the Photoseed soybean meal. The observation that the control soybean meal had greater digestibility of some indispensable AA may be an effect of the lower concentration of trypsin inhibitors in the control soybean meal compared with the Photoseed soybean meal. However, concentrations of digestible Arg, Lys, Met, and Trp were greater (P < 0.05) in the Photoseed soybean meal than in the control meal, and the concentration of digestible total indispensable AA tended (P = 0.059) to be greater in the Photoseed soybean meal than in the control soybean meal (Table 3). The reason for this observation is that the Photoseed soybean meal had a greater concentration of AA than the control meal.
Keypoints
- Photoseed soybean meal had a greater nutrient concentration compared with conventional soybean meal.
- Digestibility of some AA was reduced in the Photoseed soybean meal compared with the control soybean meal.
- Photoseed soybean meal had greater concentration of digestible Arg, Lys, Met, and Trp compared with the control soybean meal.
Table 1. Analyzed composition of the test ingredients, as-fed basis.
|
Item, % |
Photoseed soybean meal |
Control soybean meal1 |
|---|---|---|
|
DM1 |
94.63 |
94.56 |
|
GE1, kcal/kg |
4,820 |
4,760 |
|
AEE1 |
7.60 |
6.57 |
|
CP1 |
44.56 |
43.15 |
|
Lys:CP |
6.42 |
6.26 |
|
Total dietary fiber |
22.90 |
24.10 |
|
Soluble dietary fiber |
3.00 |
5.00 |
|
Insoluble dietary fiber |
19.90 |
19.10 |
|
Ash |
6.90 |
6.62 |
|
Ca |
0.36 |
0.37 |
|
Total P |
0.77 |
0.70 |
|
Phytate-P2 |
0.48 |
0.45 |
|
Nonphytate-P3 |
0.28 |
0.25 |
|
Non-phy-P, % of total P |
37.10 |
35.77 |
|
Indispensable AA |
||
|
Arg |
3.22 |
2.94 |
|
His |
1.15 |
1.09 |
|
Ile |
1.97 |
1.93 |
|
Leu |
3.31 |
3.22 |
|
Lys |
2.86 |
2.70 |
|
Met |
0.65 |
0.62 |
|
Phe |
2.19 |
2.12 |
|
Thr |
1.78 |
1.71 |
|
Trp |
0.61 |
0.57 |
|
Val |
2.06 |
1.97 |
|
Total |
19.80 |
18.87 |
|
Dispensable AA |
||
|
Ala |
1.96 |
1.87 |
|
Asp |
5.10 |
4.83 |
|
Cys |
0.71 |
0.70 |
|
Glu |
8.12 |
7.65 |
|
Gly |
2.00 |
1.87 |
|
Pro |
2.16 |
2.05 |
|
Ser |
2.00 |
1.92 |
|
Tyr |
1.67 |
1.58 |
|
Total |
23.72 |
22.47 |
|
Total AA |
43.89 |
41.69 |
|
Trypsin inhibitor5, TIU/mg |
>6.0 |
>5.3 |
|
Trypsin inhibitor, TIA (mg/g) |
>11.4 |
>10.07 |
|
Sugar profile |
||
|
Glucose |
<0.05 |
<0.05 |
|
Sucrose |
5.08 |
5.73 |
|
Maltose |
0.27 |
0.28 |
|
Fructose |
0.05 |
0.05 |
|
Stachyose |
5.05 |
5.68 |
|
Raffinose |
1.34 |
1.62 |
2Phytate-P was calculated by multiplying the analyzed phytate by 0.282 (Tran and Sauvant, 2004).
3Nonphytate-P was calculated as the difference between total P and phytate-P.
5Calculated using a conversion factor: TIU/mg = 1.9 × TI, mg/g (Hamerstrand et al. 1981).
Table 2. Standardized ileal digestibility of CP and AA in soybean expellers by growing pigs1.
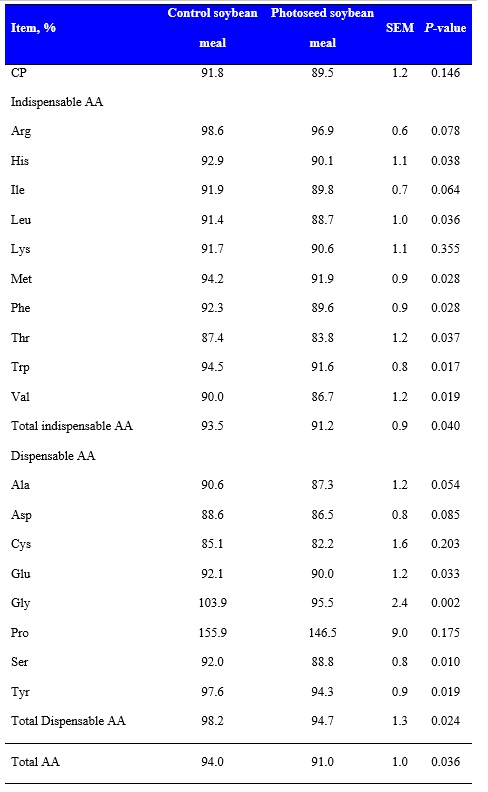
1Each least squares mean for experimental diets from growing pigs represents 9 observations, respectively.
Table 3. Concentration of standardized ileal digestible CP and AA in soybean expellers fed to growing pigs, as-fed basis1,2.
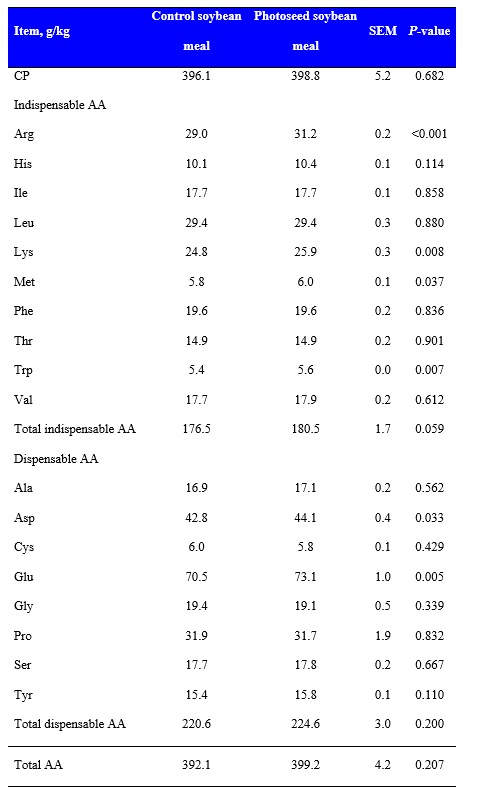
2Standardized ileal digestible concentration = Total concentration (g/kg) × SID/100.
2Each least squares mean for experimental diets from growing pigs represents 9 observations, respectively.