In most AA digestibility experiments collection bags are changed at least every 30 min and the collected ileal digesta are stored at –20 °C to prevent microbial degradation of proteins. Other attempts to reduce microbial activity in digesta include adding acids to collection bags to reduce the pH in ileal digesta. Acids may also be added to collection pitchers. However, in some experiments, no attempt to reduce pH is made because it is assumed that the rapid reduction in temperature after collection is sufficient to prevent microbial degradation of proteins.
To our knowledge, there is, however, no information about the necessity of adding acids to collected digesta and it is not known if values for apparent ileal digestibility (AID), basal endogenous losses of AA, or standardized ileal digestibility (SID) of AA are influenced by addition of acids to digesta. Therefore, the objective of this experiment was to test the null-hypothesis that values for AID, basal endogenous losses, and SID of AA are not influenced by addition of acids to ileal digesta collection bags or to collection pitchers.
Experimental design
Twenty-four barrows (initial BW: 77.8 ± 4.5 kg) that were equipped with a T-cannula in the distal ileum were used and 4 diets were formulated. Three diets contained corn, soybean meal (SBM), or wheat middlings as the only source of protein and AA, and the fourth diet was an N-free diet that was used to determine endogenous losses of AA.
The 24 pigs were allotted to 4 diets and 3 periods. Thus, 6 pigs were fed each diet in each period. Digesta from 3 pigs were collected in bags containing no HCl whereas 40 mL of 3N HCl was included in the bags used to collect digesta from the remaining 3 pigs. Following collection, digesta bags were alternately emptied into collection pitchers without adding HCl or into pitchers along with 40 mL of 3N HCl for each bag. All pitchers were stored at –20 °C at all times. Therefore, for pigs fed the 3 diets containing corn, SBM, and wheat middlings, there were a total of 12 treatments arranged in a 3 × 2 × 2 factorial with feed ingredients (i.e., corn, SBM, and wheat middlings) as the first factor and no HCl or addition of HCl in either collection bags or collection pitchers as the second and third factors, respectively. For pigs fed the N-free diet, there were 4 treatments that were arranged in a 2 × 2 factorial with no HCl or addition of HCl in either collection bags or collection pitchers. Three replicate pigs were used per treatment in each period and there were a total of 9 replications per treatment. The initial model included the fixed effects of feed ingredients, HCl in collection bags, HCl in collection pitchers, and all 2-way and 3-way interactions. The random effects were HCl in collection bags and square, period, and pig nested within HCl in collection bags. However, no 3-way interactions were significant (P > 0.10), and data were, therefore, analyzed independently for each diet as a 2 × 2 factorial using the same split-plot arrangement as used for the initial model.
Results
For corn, SBM, and wheat middlings, there were no interactions between HCl in collection bags and in collection pitchers for the AID of all AA. No effects of adding HCl to collection bags or collection pitchers for the AID of AA in corn, SBM, or wheat middlings were observed with the exception that the AID of Met in wheat middlings was greater (P = 0.049) if HCl was added to bags compared with no HCl in the bags. The AID of Pro and total dispensable AA in wheat middlings were also greater (P < 0.05) if HCl was added to collection pitchers than if no HCl was added.
No interactions between the addition of HCl to collection bags and collection pitchers were observed for basal endogenous losses of AA (Table 1). There were also no effects of adding HCl to either collection bags or collection pitchers.
No interactions between adding HCl to collection bags and pitchers for the SID of AA in corn were observed, and there were no effects of adding HCl to either collection bags or pitchers in the SID of AA in corn (Table 2). For SBM, no interactions between adding HCl to collection bags and pitchers for the SID of AA except for Arg were observed (Table 3). If no HCl was added to collection bags, the SID of Arg in SBM was less (P < 0.05) if HCl was added to collection pitchers than if no HCl was added, but if HCl was added to collection bags, there were no differences between adding HCl and no HCl to collection pitchers (interaction; P < 0.05). Addition of HCl to collection bags did not change values for SID of most AA in SBM and there were no effects of adding HCl to collection pitchers with the exception that the SID of Met was greater (P = 0.041) if HCl was added to collection pitchers than if no HCl was added to pitchers. For the SID of AA in wheat middlings, no interactions between adding HCl to collection bags and pitchers were observed (Table 4). Adding HCl to either collection bags or collection pitchers did not affect the SID of AA.
In conclusion, if digesta are stored at –20 °C immediately after collection, there are no clear advantages of adding HCl to digesta collection bags or collection pitchers on values for the basal endogenous losses of AA and the AID and SID of most AA.
Key points
- No interactions between adding HCl to collection bags and collection pitchers for the basal endogenous losses and the SID of most AA in corn, SBM, and wheat middlings were observed.
There are no clear advantages of adding HCl to digesta collection bags or collection pitchers on values for the basal endogenous losses of AA and the AID and SID of most AA.
Table 1. Basal endogenous losses of AA (g/kg dry matter intake) without or with 40 ml of 3N HCl in the collection bag or the collection pitcher
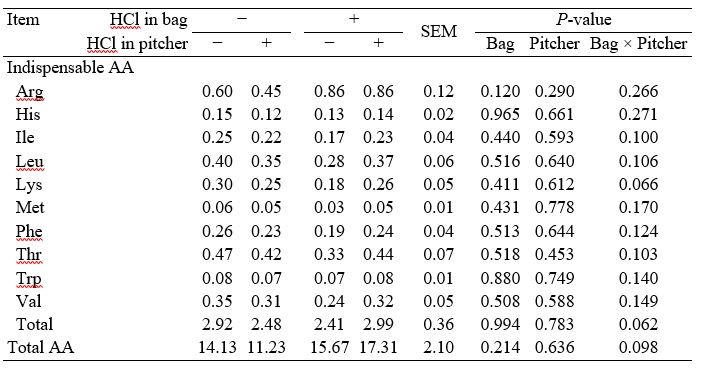
Table 2. SID of AA in corn without or with 40 ml of 3N HCl in the collection bag or the collection pitcher1
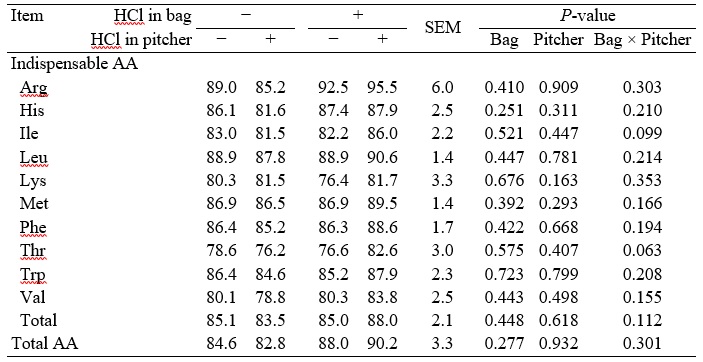
Table 3. SID of AA in SBM without or with 40 ml of 3N HCl in the collection bag or the collection pitcher1
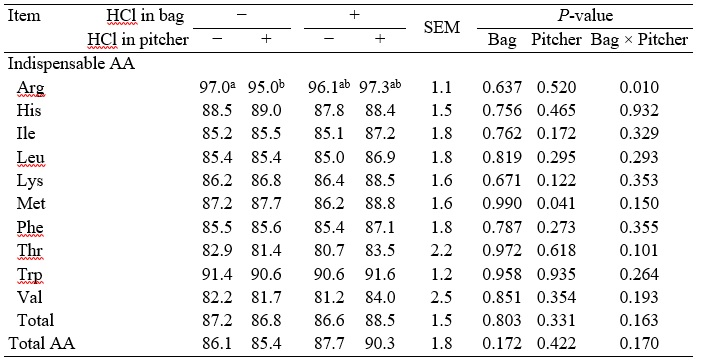
a-bWithin a row, means lacking a common superscript letter differ (P < 0.05).
1Within treatment values for SID were calculated by correcting AID values for basal ileal endogenous losses determined from ileal digesta that was treated or not treated with HCl in a similar way.
Table 4. SID of AA in wheat middlings without or with 40 ml of 3N HCl in the collection bag or the collection pitcher1
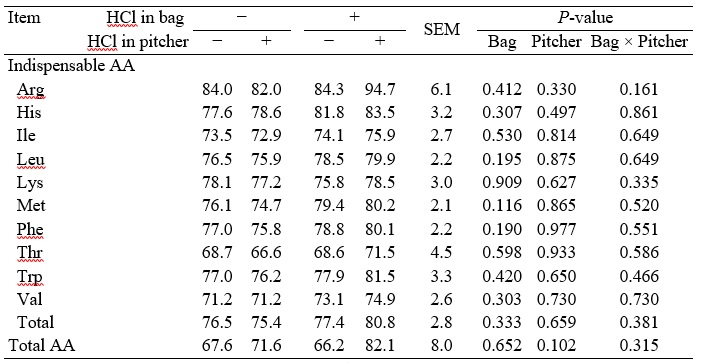
1Within treatment values for SID were calculated by correcting AID values for basal ileal endogenous losses determined from ileal digesta that was treated or not treated with HCl in a similar way.